How to Increase Your Network Attached Storage (NAS) Speed and Performance?

Introduction:
It is very common to use a network attached storage as a central file sharing and collaboration, where there are several devices accessing files and resources on your NAS simultaneously.
However, everything has a limit, and while in most use cases, the performance of your NAS can be enough for limited usage, there will be a need to optimize and fine-tune things to make it even better.
What can be done to increase NAS performance?
Well, much like every device that runs an operating system, specifically servers, the network attached storage has multiple areas where it can be optimized.
Obviously, Hardware specifications are a crucial aspect of performance optimization.
Also, Network Optimization is an important area for NAS Storage that is accessed on a local network
There are also less obvious areas, like configurations and settings or storage settings.
What factors can affect NAS Speed or Performance?
There are lots of factors that directly affect the performance of Your NAS, some more effective than others.
Most notably is the Hardware Factors, it’s the first thing that you look at when you buy any device, even before you open and use the device.
There are also Software and Network factors. Let’s check them in detail:
Hardware Specs:
- Processor and RAM capabilities:
this is the first thing you look at. CPUs can vary according to the number of cores, clock speed, and caching mechanism. Also the RAM memory comes with various types and capacities (DDR3 , DDR4, etc…).
- SSD and HDD drives: using SSD drives boosts the performance much more than HDD drives
Network Infrastructure:
- LAN Speed has a big impact on Data transfer from and to the NAS,
- Using 10Gbps switches and routers with Cat6 or Cat7 Cables will improve the network performance.
Software and Configurations:
- RAID configuration will affect the performance.
- The number of concurrent users
- The services running on the NAS (Media Streaming, Backups, etc..)
Tips to Increase NAS Performance and Optimize it:
Hardware Optimization:
1) Change Hardware Components:
When possible, you can add more RAM Memory to increase the NAS capacity.
Additionally, you can make sure to use SSD drives, although it’s more costly, it increases the read/write speeds drastically.
2) Choose the right RAID configurations:
RAID configuration types are different in purpose, write speed and read speed, however you can balance between these speeds according to your needs:
| RAID Type | Minimum Drives | Fault Tolerance | Storage Efficiency | Read Speed | Write Speed | Best Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RAID 0 | 2 | None | 100% | Very High | Very High | High-performance tasks, non-critical data |
| RAID 1 | 2 | 1 Drive Failure | 50% | Moderate | Moderate | Data redundancy, important small-scale storage |
| RAID 5 | 3 | 1 Drive Failure | 66.6%-94.5% | High | Moderate | File servers, databases, moderate performance and redundancy |
| RAID 6 | 4 | 2 Drive Failures | 50%-90% | High | Lower than RAID 5 | High redundancy needs, critical storage |
| RAID 10 | 4 (2 pairs) | 1 Drive per Pair | 50% | Very High | High | High performance and redundancy (databases, virtual machines) |
| RAID 50 | 6 (2 sets of RAID 5) | 1 Drive per RAID 5 set | 70%-90% | Very High | Moderate to High | Large storage with balance of performance and redundancy |
3) Ensure you have enough storage:
Plan the capacity of the storage you need, also take into account the storage after implementing RAID configurations.
Network Optimization:
1) Use 10Gbps Network Components:
Using 10Gbps Switches and Routers, along with Cat6 Or Cat7 Cables.
2) Enable Link Aggregation:
Most NAS devices that have more than one Network Interface, usually support Link Aggregation features.
This feature combines multiple network interfaces so they act as one single interface.
Let’s enable link aggregation on Qnap NAS as an example:
On Qnap Management Portal, Open control panel > Network & virtual Switch:
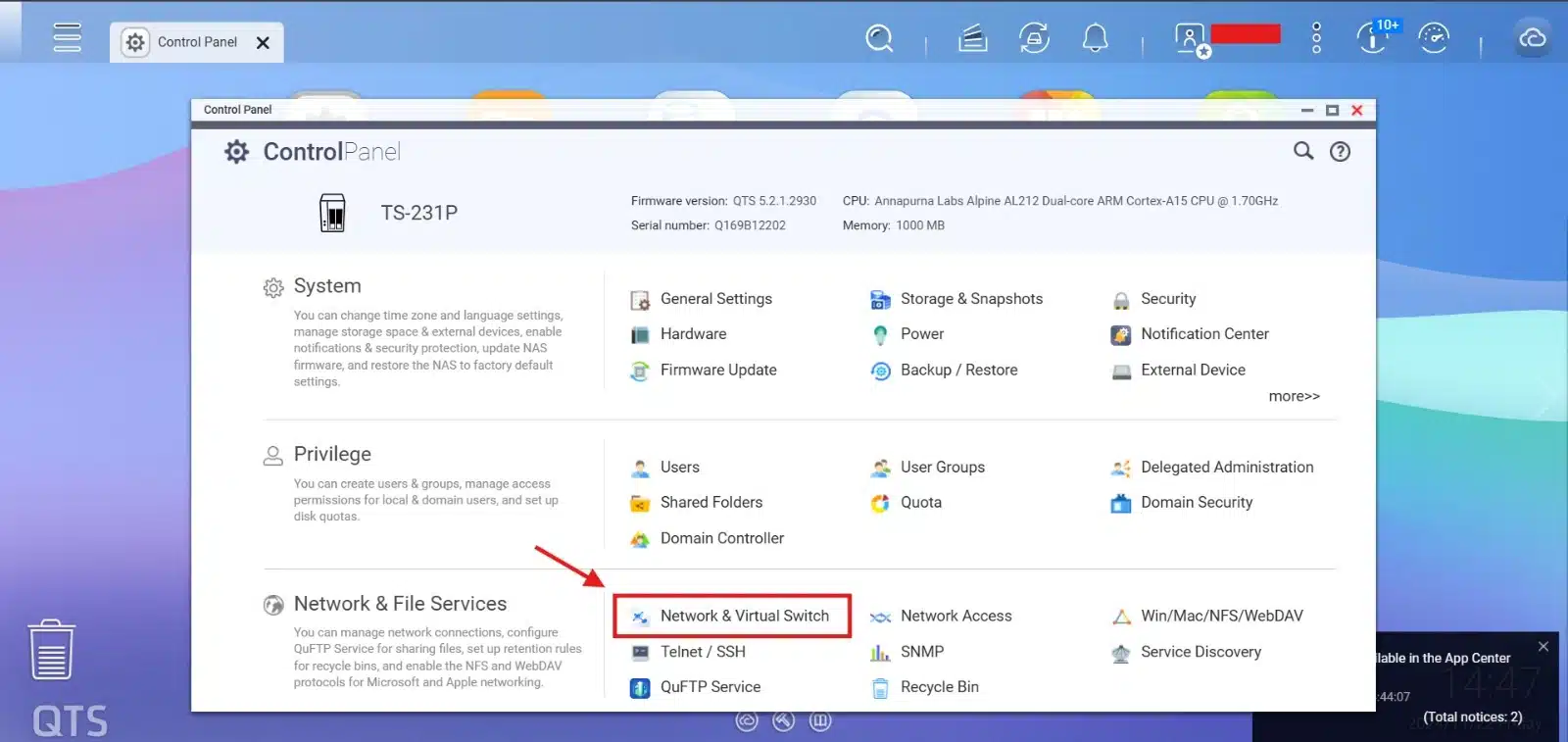
Then go to “Interface” and click on “+ Port Trunking”:
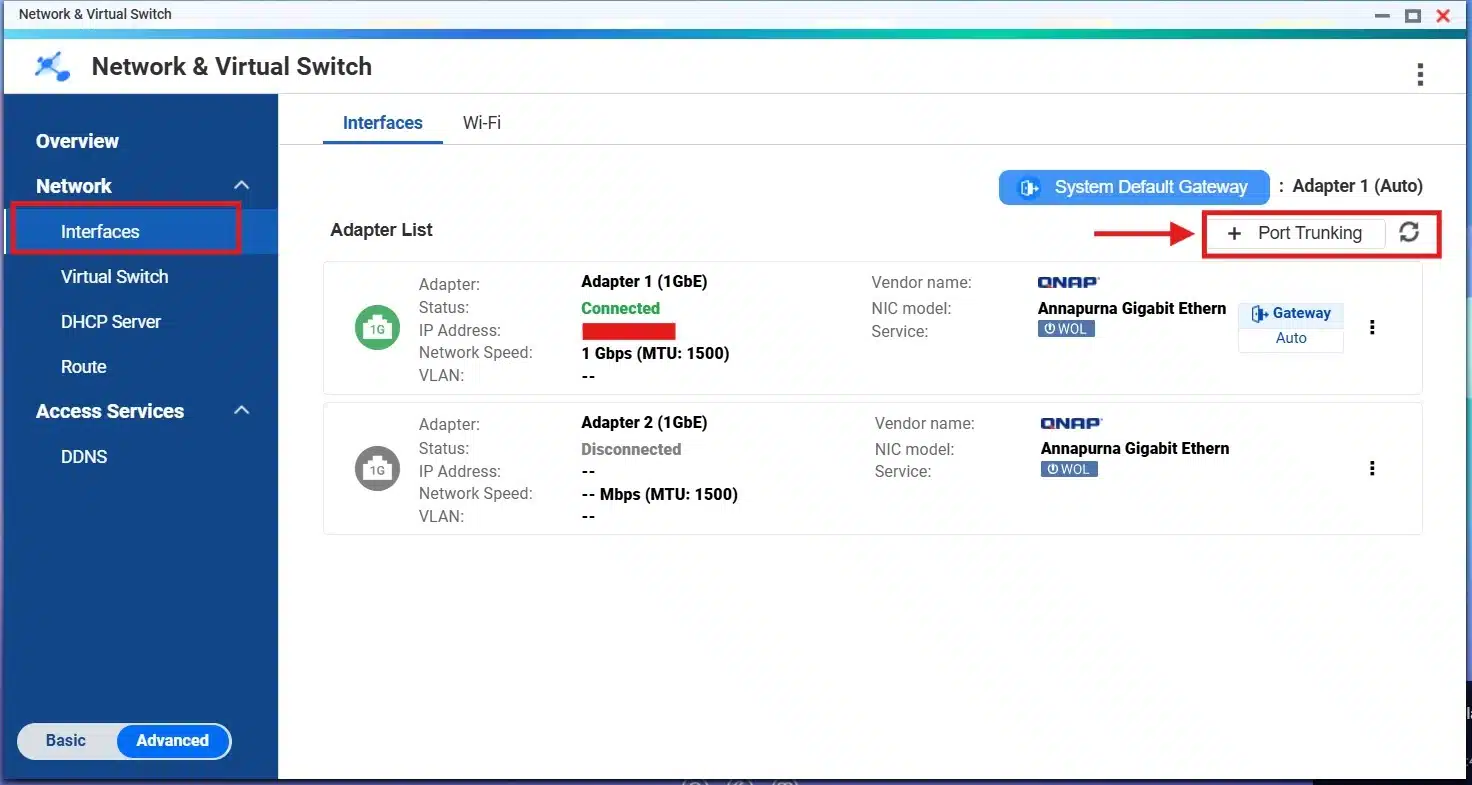
Click on “Add” to add a new port trunking:
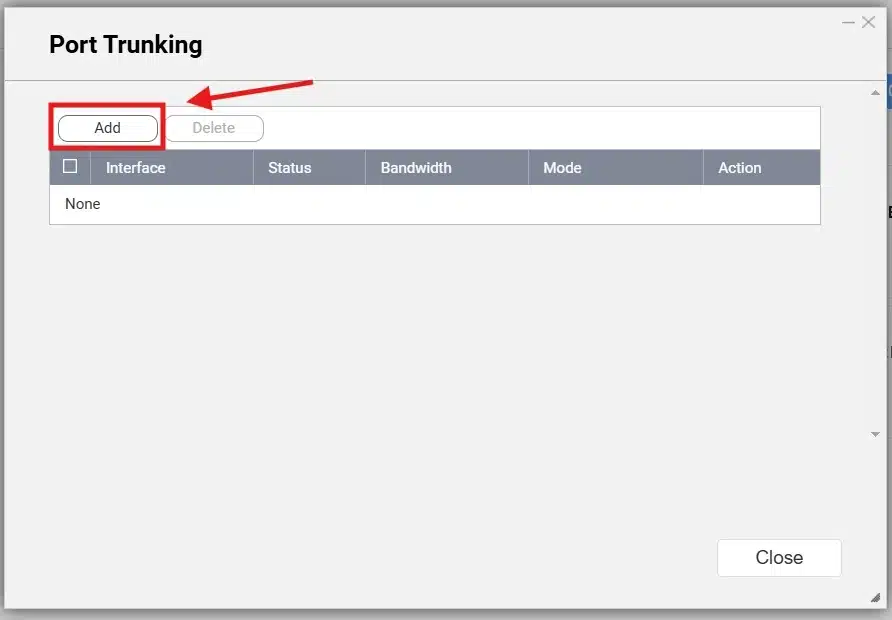
Choose the interfaces you want to add to the port trunking, then click “Next”:
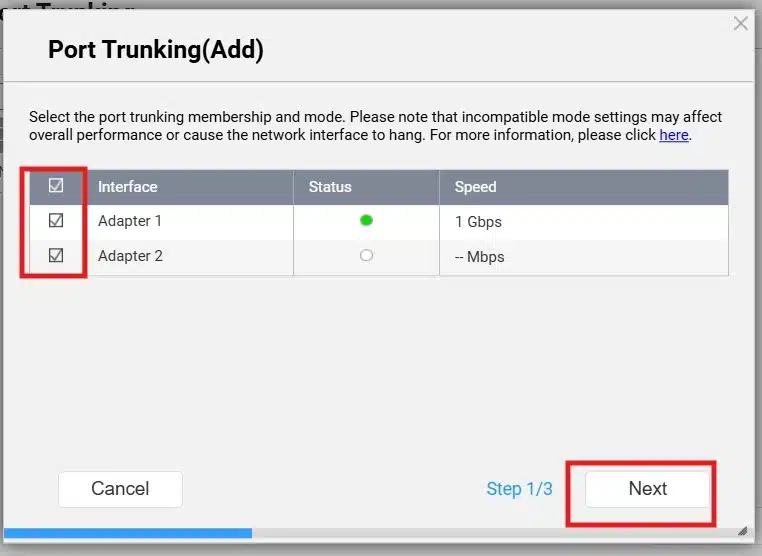
Here you can choose which Switch Type according to the mode you want to implement:
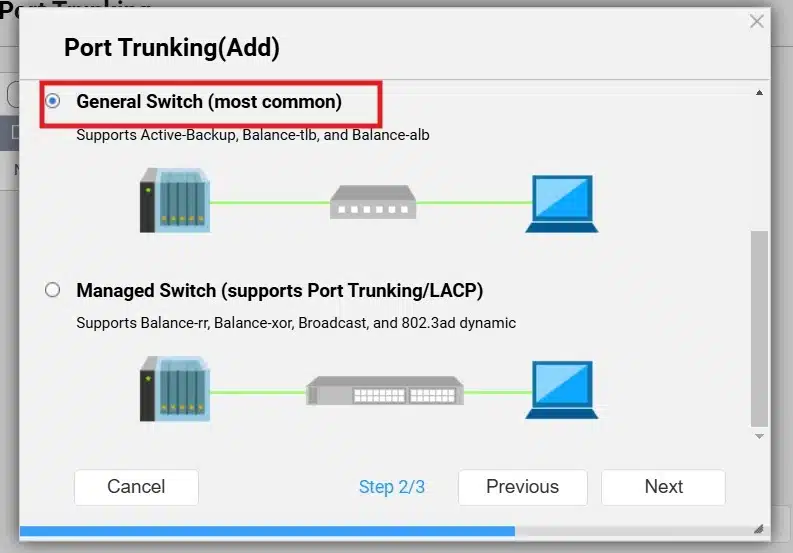
Now, choose which mode you need, I will choose “Balance-alb” as it supports load balancing for incoming and outgoing traffic. Then click “Apply”.
For information about Trunking modes, check out Qnap Documentation:
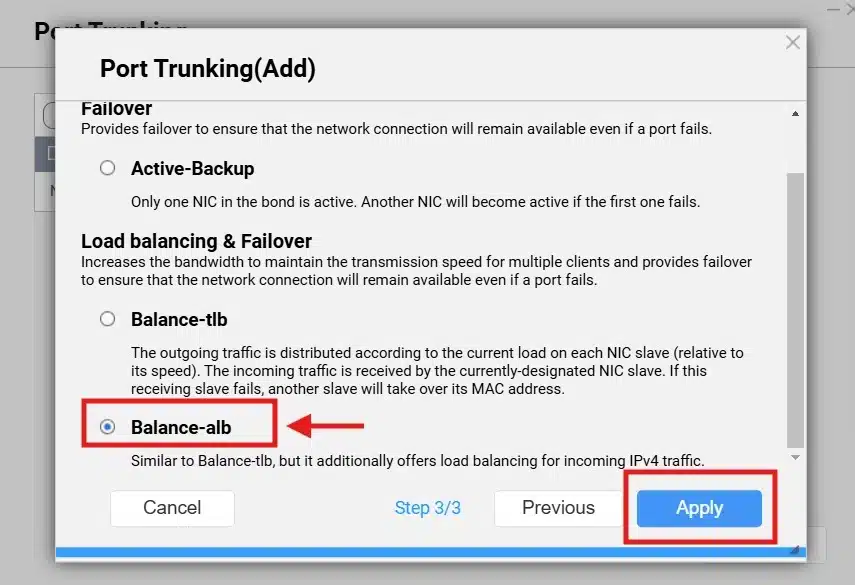
*Note: once you click apply, it might warn you that the page will reload and will be redirected to the new IP automatically.
Now we have Trunking Port and showing “Adapter 1+2:
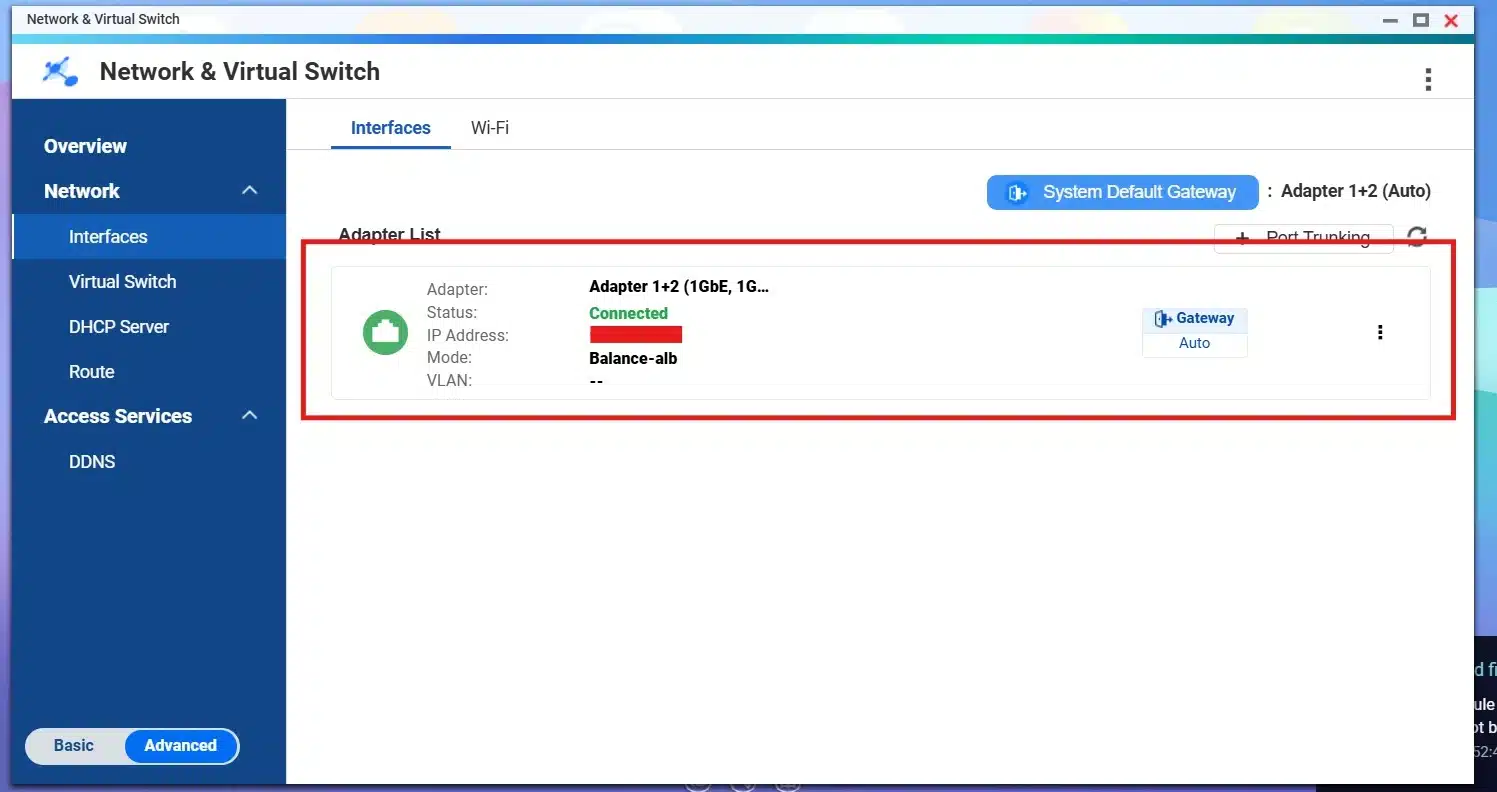
This trunk acts as one interface, so it gets one IP Address, but you can configure it and assign a static IP Address to it:
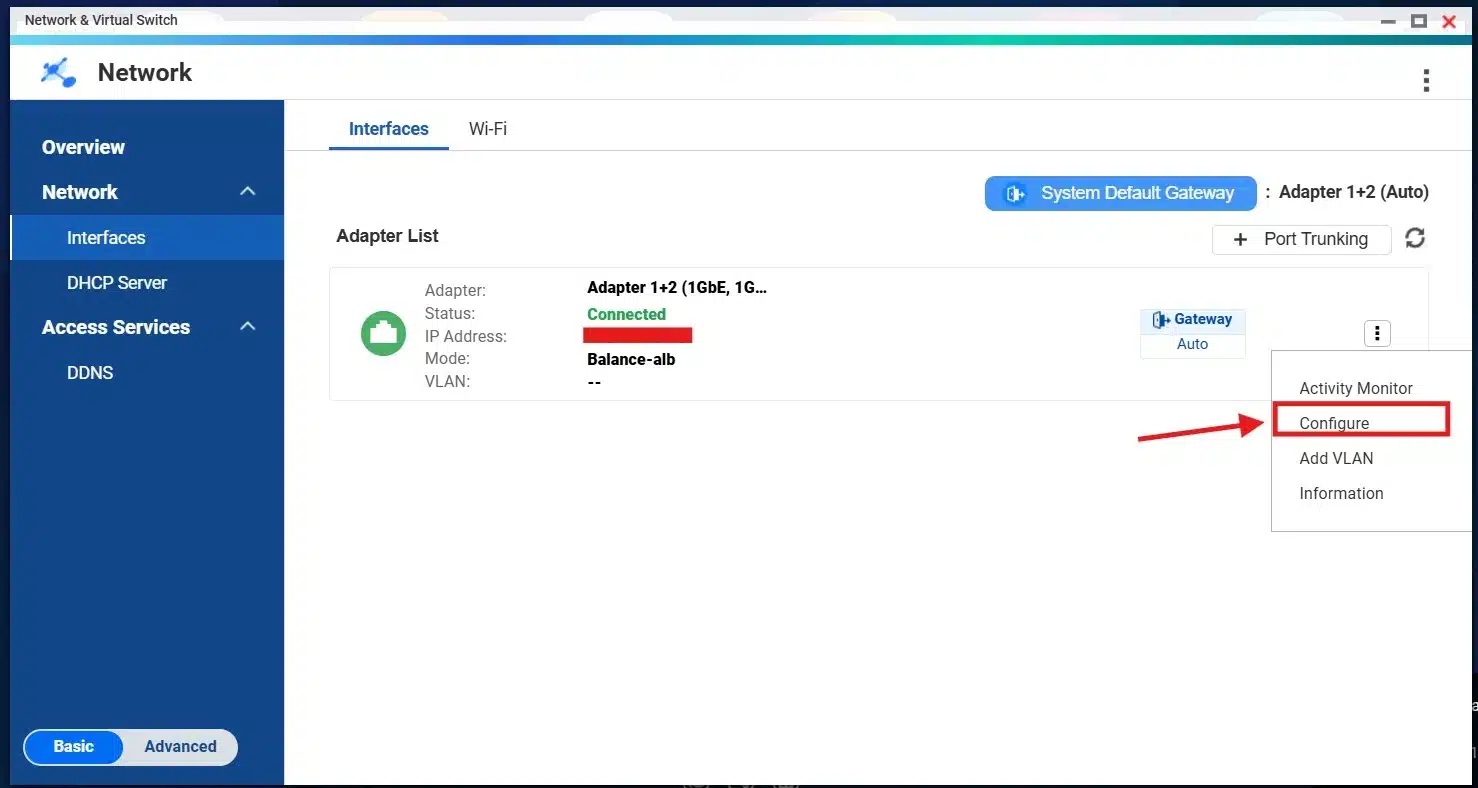
3) Use Network Optimization Techniques:
When possible you can optimize your network to enhance the traffic in and out of your NAS:
– Implement Quality of Services (QoS): QoS will help you prioritize the traffic on your NAS over the network
– NAS Physical Position: try to place the NAS Device physically close to the router, basically using the shortest cable possible.
Software and Configurations Optimization:
Backup Strategy:
– optimize your Backup Jobs by using backup software that supports Incremental Backup or Differential Backup like (Veeam, Qnap HBS3 Hybrid Backup , Synology Active Backup, etc…).
– Always Schedule Backups outside the active hours, schedule it when your network is not busy and the traffic is minimal.
System Settings:
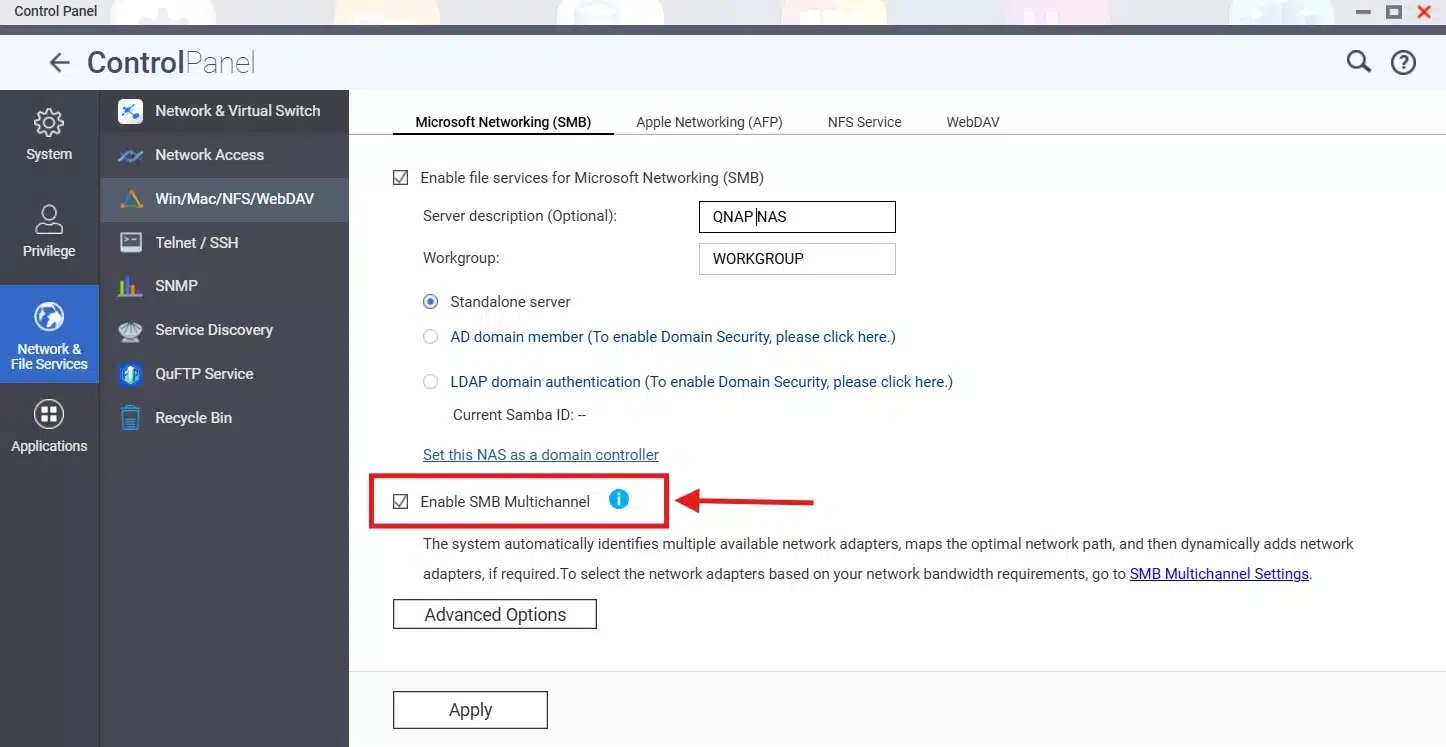
– SMB multichannel: if you are using SMB to access NAS over the network on windows machines, enabling SMB multichannel can increase file transfer by identifying the optimal path through multiple network adapters ( this will not be useful if you are already using link aggregation ).
To enable SMB Multichannel on your Qnap NAS:
Open control panel > Win/Mac/NFS/WebDAV, then on the “Microsoft Networking (SMB)”, make sure to check the option “Enable SMB Multichannel”:
– SSD cache: consider using ssd cache on your NAS by adding an SSD drive if your NAS supports it.
For more information about SSD Cache, check out SSD-Caching
Maintenance and Monitoring:
– Keep your NAS Firmware up to date: enable automatic update to ensure getting updates directly.
– Replace Any Drive when it’s failed: ensure your RAID configurations are at full potential.
– Check Drives Health: use the build-in and Manufacturer-Provided tools to regularly checking your Drives.
– Use Built-in tools on Your NAS to monitor System resources like network, CPU, Memory and Storage Activity.
Conclusion:
Optimizing your NAS ensures faster performance and reliability, especially for heavy workloads or multi-device access. Simple upgrades like adding RAM, using SSDs, improving network speed, and enabling features like Link Aggregation or SMB Multichannel can make a big impact. Regular maintenance and tailored configurations further enhance efficiency.





